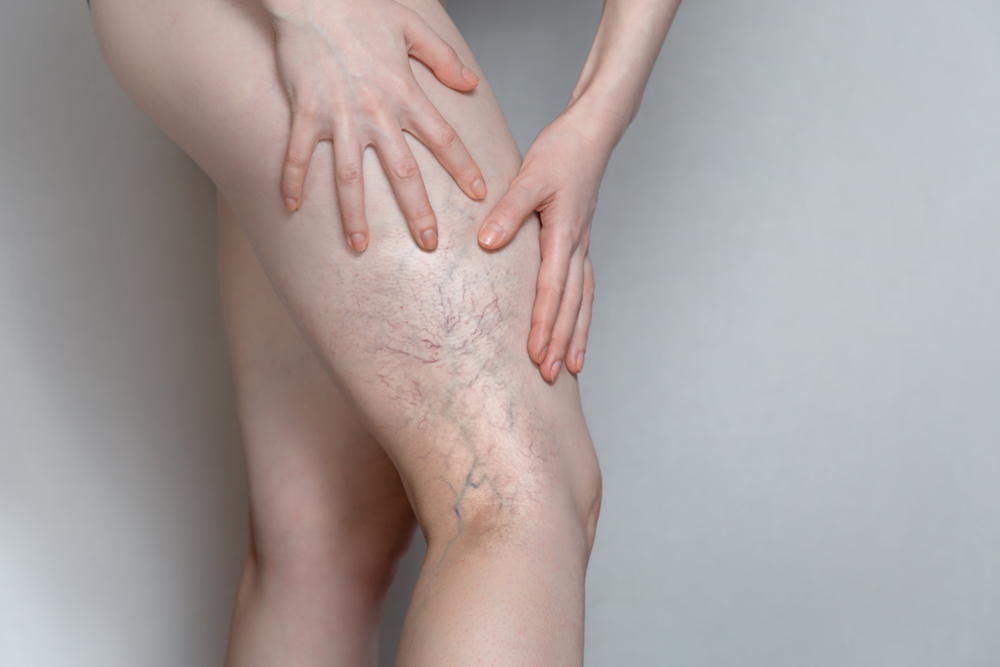
Beyond their unsightly appearance and discomfort, varicose veins can be an indicator of more serious vein-related complications. One of these complications is superficial thrombophlebitis.
What Is Superficial Thrombophlebitis?
Superficial thrombophlebitis occurs from a blood clot, often in leg veins, that causes inflammation of the vein just below the skin’s surface. While it most commonly affects superficial leg veins closest to the skin, superficial thrombophlebitis can also develop in the groin or arms.
Symptoms
There are several common symptoms associated with superficial thrombophlebitis. The skin above the affected vein will become red and tender, and often warm to the touch. Superficial Thrombophlebitis can also cause pain in the limb in which the clot has developed. Because the vein is clotted, the area of the clot or the entire vein may feel hard and cord-like, unlike varicose veins, which remain soft.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis and treatment require a consultation with a vein specialist. A phlebologist can diagnose superficial thrombophlebitis by its appearance. Depending on the severity and rate at which superficial thrombophlebitis developed, the doctor may perform an ultrasound to determine if there is a blood clot deeper in the vein.
Treatment
While superficial thrombophlebitis often subsides on its own, there are several treatments you can perform to reduce the symptoms and accelerate your recovery. To provide immediate relief, a doctor may inject a local anesthetic and remove the clot. Applying warm compresses to the affected area and taking an NSAID pain reliever like ibuprofen will also help reduce the pain and inflammation. Inflammation often subsides in a few days, but it may take several weeks for the lumps and tenderness to subside completely. Other recommendations include compression stockings, aspirin, and exercise.
Further Complications
While not especially serious on its own, superficial thrombophlebitis can sometimes lead to more serious complications, such as deep vein thrombosis, where blood clots occur deeper in the vein. With DVT, there is a higher risk of the blood clot breaking off and causing life-threatening complications, such as a pulmonary embolism.
As a primary cause of superficial thrombophlebitis, varicose veins should be addressed as soon as they develop. If you have symptoms of superficial thrombophlebitis or varicose veins, schedule a free consultation online here or call 512-220-5401.